Following schema describes the access to application ABC. Access to the application ABC is managed via membership of LDAP groups. One user has access to the application configured directly in the application.
Access model of the application ABC:
-
members of ABC_R LDAP group have Reader access level to application ABC,
-
members of ABC_E LDAP group have Editor access level to application ABC,
-
members of ABC_M LDAP group have Manager access to application ABC,
-
user Clark Cooper has Manager access to application ABC.
User Adam Smith is member of ABC_R LDAP group and user Buster Blake is member of ABC_M group. These groups give them access to application ABC.
Environment and configuration of midPoint can be described by following picture:
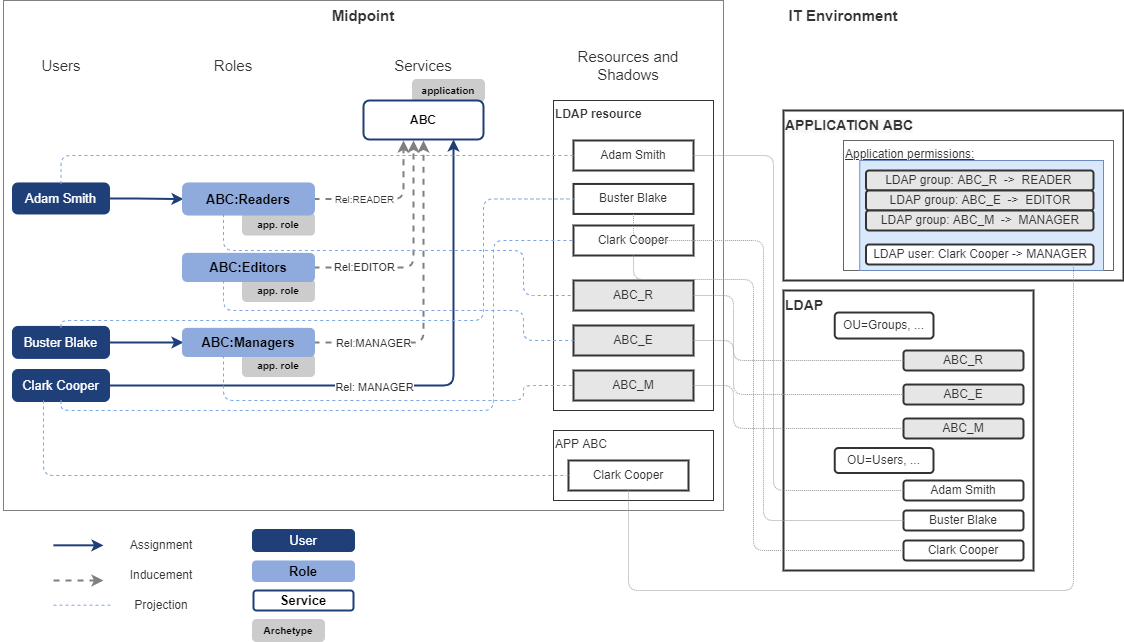
Application access model
Access model of application ABC is represented by roles directly induced to ABC service representing application and direct assignment of the ABC service to user Clark Cooper. Relations are describing business description of access level.
Such midPoint configuration may be interpreted by technical (IAM) language or by business language.
Technical interpretation (IAM):
-
Adam Smith has role ABC:Readers assigned. Therefore he has account in LDAP_resource and is assigned in _ABC_R LDAP group. He has service ABC assigned.
-
Buster Blake has role ABC:Managers assigned. Therefore he has account in LDAP_resource and is assigned in _ABC_M LDAP group. He has service ABC assigned.
-
Clark Cooper has service ABC assigned.
This technical interpretation explains information necessary for provisioning, but will not tell much about user access to the application without additional knowledge of application access model.
Business interpretation (IGA):
This interpretation describes user access to the application. Clearly understandable by business.
-
Adam Smith has Reader access to application ABC via application role ABC:Readers.
-
Buster Blake has Manager access to application ABC via application role ABC:Managers.
-
Clark Cooper has Manager access to application ABC.